U.S. citizens and resident aliens living abroad often face challenges in meeting standard tax filing deadlines. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) recognizes this and provides certain reliefs, including Form 2350. This form gives taxpayers abroad additional time to establish eligibility for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) before filing their return.
This article explains what IRS Form 2350 is, who must file it, how to complete and submit it, and key rules taxpayers should know.
What is IRS Form 2350?
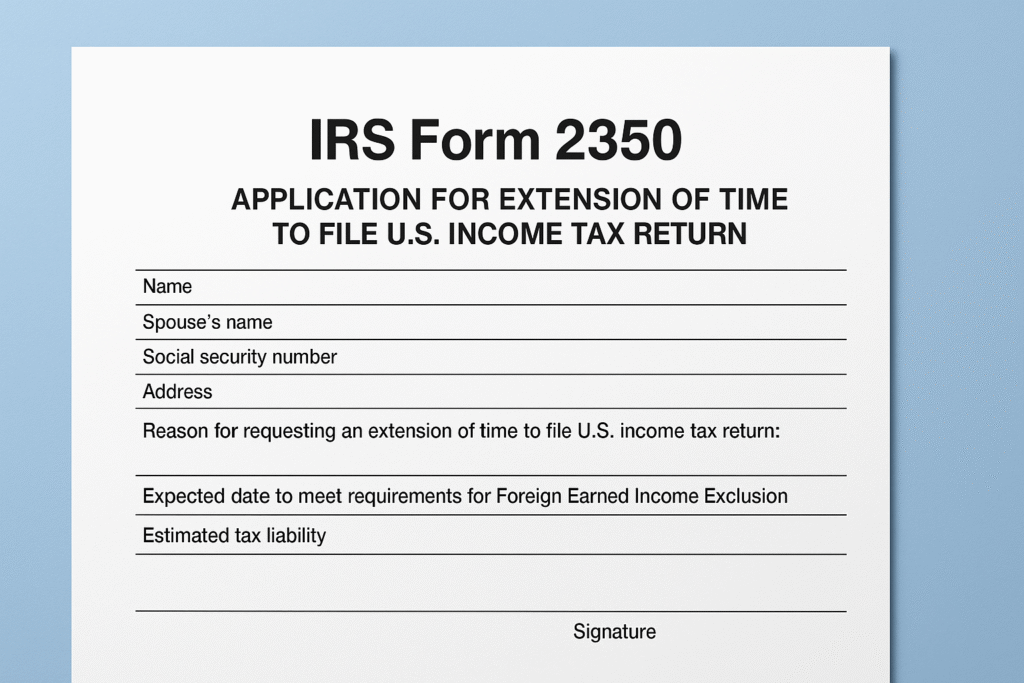
IRS Form 2350, Application for Extension of Time to File U.S. Income Tax Return, allows taxpayers abroad to request an extension beyond the regular deadline. Unlike Form 4868, which provides a general six-month extension, Form 2350 applies specifically to taxpayers waiting to qualify for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE).
The form gives additional time to meet either the Bona Fide Residence Test or the Physical Presence Test, both of which determine FEIE eligibility.
Who Must File Form 2350?
Taxpayers should file Form 2350 if they meet these conditions:
- They are U.S. citizens or resident aliens.
- They live or work outside the United States.
- They expect to qualify for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE).
- They cannot file a timely return because they are still in the process of meeting the Bona Fide Residence Test or Physical Presence Test.
This form is not intended for those who already meet FEIE requirements by the April or June deadlines.
Understanding the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE)
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) allows qualifying taxpayers to exclude a set amount of foreign income from U.S. taxation.
- 2025 Exclusion Limit: Up to $120,000 of foreign earned income.
- Purpose: Prevents double taxation and provides relief for Americans working abroad.
- Eligibility Tests:
- Bona Fide Residence Test – Establishes residence in a foreign country for an entire tax year.
- Physical Presence Test – Requires physical presence in a foreign country for at least 330 full days during any 12-month period.
Taxpayers often file Form 2350 to delay filing until one of these tests is met.
Key Considerations for Businesses and Investors
Form 2350 benefits more than just employees abroad.
- Business Owners: Self-employed individuals working overseas can request additional time to qualify for FEIE and avoid rushed or incomplete filings.
- Investors: Individuals earning dividends, rental income, or interest abroad may use Form 2350 to extend filing while ensuring proper reporting.
- Tax Planning: Businesses and individuals abroad gain more flexibility in coordinating FEIE with other tax benefits such as the Foreign Tax Credit (Form 1116).
IRS Form 2350 Due Date and Timeline
- Regular tax deadline: April 15.
- Automatic extension for expats: June 15.
- Form 2350 extension: May extend the filing date beyond June 15 until the taxpayer qualifies for FEIE.
Important: Form 2350 extends only the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. Tax owed must still be paid by April 15 to avoid interest charges.
Information Required to File Form 2350
When preparing Form 2350, taxpayers need:
- Full name, Social Security Number, and foreign address.
- The applicable tax year.
- Explanation of why more time is needed (FEIE eligibility).
- The expected date to meet FEIE requirements.
- Estimated tax liability and payments already made.
- Signature and date of submission.
Step-by-Step: How to Complete Form 2350 (Line by Line)
- Name and Address: Provide personal information and foreign residence details.
- Tax Year: Enter the calendar year for which the extension is requested.
- Reason for Request: State that additional time is needed to meet FEIE eligibility.
- Expected Qualification Date: Estimate when the Bona Fide Residence or Physical Presence test will be satisfied.
- Estimated Tax Due: Calculate total tax expected for the year.
- Payments Made: Enter any taxes already paid or withheld.
- Balance Due: Subtract payments from the estimated liability.
- Signature: Sign and date the form before mailing.
Filing Methods: How to Submit Form 2350
Form 2350 must be filed on paper. It cannot be e-filed. Taxpayers should:
- Mail the completed form to the IRS.
- Attach a check or money order for any balance due.
- Retain a copy of the form for records.
IRS Mailing Address for Form 2350
Mail Form 2350 to:
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
Austin, TX 73301-0215
USA
Taxpayers should confirm the latest mailing address on the IRS website before submission, as addresses may change.
Penalties for Missing the Form 2350 Deadline
Failure to submit Form 2350 on time may result in:
- Late filing penalty: 5% of unpaid tax per month, up to 25%.
- Interest charges: Accrued from April 15 until payment.
- Loss of FEIE eligibility: If deadlines are missed, taxpayers may lose the opportunity to exclude foreign earned income.
FAQs About IRS Form 2350 and Expat Taxes
What is the Bona Fide Residence Test?
The Bona Fide Residence Test applies when a taxpayer lives in a foreign country for an entire tax year with no definite plans to return to the U.S. immediately.
What is the Physical Presence Test?
This test requires taxpayers to be physically present in a foreign country for at least 330 full days within a 12-month period.
What is the difference between Form 4868 and Form 2350?
- Form 4868: Provides a general six-month filing extension for U.S. taxpayers.
- Form 2350: Specifically grants extra time to taxpayers abroad who need to qualify for FEIE.
What is the Foreign Tax Credit and how to claim it?
The Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) reduces U.S. tax liability by allowing a credit for taxes paid to foreign governments. Taxpayers claim it using Form 1116.
Can you claim the Foreign Tax Credit if you don’t qualify for FEIE?
Yes. Taxpayers unable to use FEIE may still offset U.S. tax liability through the Foreign Tax Credit, ensuring relief from double taxation.
Conclusion
IRS Form 2350 serves a vital role for Americans abroad. It allows taxpayers more time to qualify for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, ensuring accurate reporting and avoiding penalties. By filing on time, expats gain flexibility in tax planning and safeguard their ability to claim valuable benefits such as FEIE or the Foreign Tax Credit.